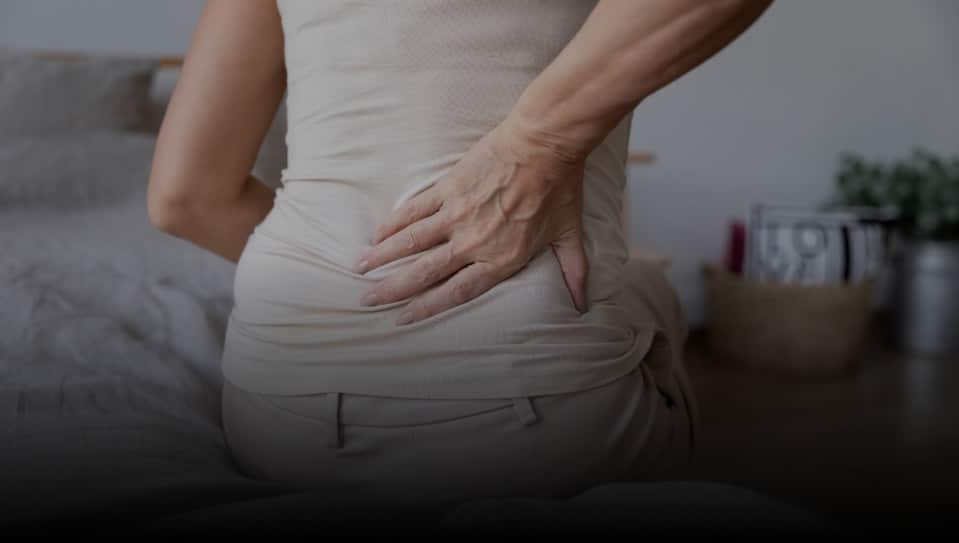
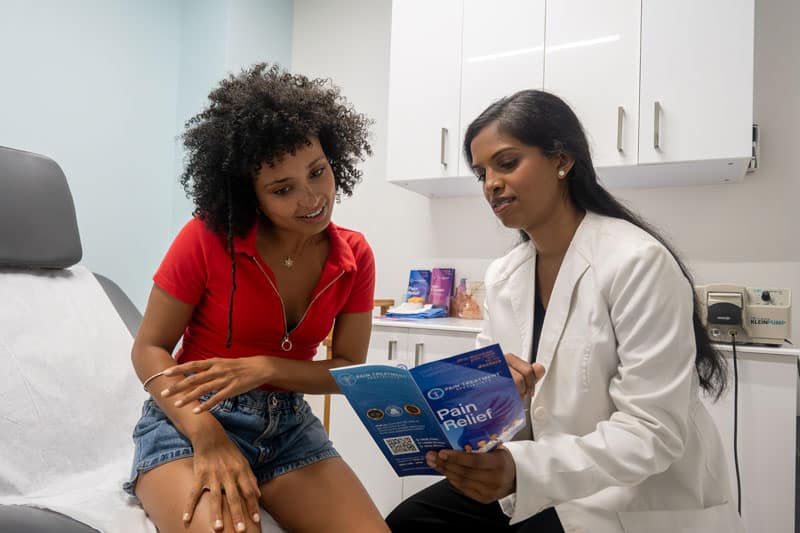
What are the best osteoarthritis treatments?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a condition that causes the cartilage in your joints to break down. This can lead to pain and stiffness. While there is no cure for OA, there are treatments that can relieve the symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. There’s no such thing as the “best treatment for osteoarthritis” because everyone is unique. The best osteoarthritis treatment for you will depend on your unique symptoms, the location of osteoarthritis flare-ups, and other factors. Below, we describe some of the best osteoarthritis treatments.
Back Center New Jersey is a group of state-of-the-art medical centers specializing in back pain treatments. Our board-certified interventional pain doctors carefully examine your affected areas, discuss your symptoms, and administer cutting-edge imaging techniques to identify the root cause of back pain. After a thorough evaluation, our back pain doctors curate a personalized osteoarthritis treatment plan consisting of non-surgical, minimally invasive treatments. You can find our centers in Clifton, Paramus, West Orange, and Woodland Park. Please schedule an appointment at your nearest back center in New Jersey.

#1. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Medications (NSAIDs)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are over-the-counter medications that can relieve pain and inflammation. NSAIDs can effectively alleviate the symptoms of osteoarthritis, a condition that causes the deterioration of the cartilage that cushions the joints. When the cartilage breaks down, the bones rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. NSAIDs reduce inflammation to alleviate pain and discomfort.
#2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a key component of osteoarthritis management. The goals of physical therapy for osteoarthritis are to reduce pain, improve joint function, increase range of motion, build muscle strength, increase endurance, improve balance and coordination, reduce stress on joints, and manage weight. Based on your individual needs and goals, your physical therapy may include exercises, manual therapy, joint protection, and heat/cold therapy.
#3. Occupational Therapy
If you have osteoarthritis (OA), you know that the pain can make it hard to do the things you love. Even simple things can become a challenge, like walking the dog or cooking dinner. Occupational therapy aims to help you stay as independent as possible. We find ways to help you do what you want, whether getting dressed in the morning, cooking dinner, or working at a job. We also work with you to prevent joint damage by creating customized exercise programs.
#4. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a therapy that uses low-voltage electrical current to relieve pain. The electrical current stimulates the nerves and blocks the pain signals from reaching the brain. TENS also stimulates the release of pain-relieving chemicals in the brain that alleviate your symptoms. Studies have found that TENS can significantly reduce osteoarthritis pain, improve a patient’s quality of life, and decrease reliance on pain medications.
#5. Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are one option for treating the symptoms of osteoarthritis. They can relieve pain and swelling in the affected joint. The injections are usually given every four to six weeks; most people will have three to five injections over a year. Corticosteroid injections reduce inflammation in the joint to improve the range of motion and reduce pain, helping you prevent or delay the need for joint replacement surgery.
#6. Viscosupplementation
Viscosupplementation is a type of injection used to treat osteoarthritis. The injection is made up of a gel-like substance called hyaluronic acid, a natural substance found in the body that lubricates and cushions joints. Viscosupplementation restores natural lubrication to the worn-down cartilage, allowing it to cushion your joints again.
Which type of doctor treats arthritis?
Most types of arthritis are chronic, meaning they last for a long time, and there is no cure. But some treatments can help lessen the pain and improve joint function. If you have the signs and symptoms of arthritis, you must contact interventional pain doctors in New Jersey.
Interventional pain doctors are medical doctors who have completed pain management fellowship training. They may also be board-certified in interventional pain management, indicating their advanced expertise. They use a variety of techniques to diagnose and treat pain. Interventional pain doctors can perform injections, nerve blocks, and other minimally invasive treatments to relieve pain, allowing you to lead a pain-free life without opioids or surgical intervention.
Does Humira treat osteoarthritis?
Yes, Humira (adalimumab) is a prescription medication for osteoarthritis. It’s a type of biologic, meaning it’s made from living cells and can stimulate your body’s ability to regenerate and heal from within. Studies have shown that Humira can reduce pain and gradually improve the symptoms of osteoarthritis. However, Humira should ideally be combined with other minimally invasive treatments, such as corticosteroids and viscosupplementation. Your back pain doctor will evaluate you thoroughly to determine if you’re a good candidate for Humira.
What should you not do with osteoarthritis?
There are a few things that you should not do if you have osteoarthritis.
- You should not try to “tough it out” and ignore the pain. This will only worsen the pain and can further damage your joints.
- You should not stop moving altogether. While it is important to rest your joints, you should not stop moving as this can lead to stiffness and more pain.
- You should not wait to seek treatment. The sooner you start treating your osteoarthritis, the better your chances are of reducing pain and maintaining joint function.